- LangChain은 LLM 애플리케이션 개발 프레임워크이다.
- LangChain 전체 구조는 다음과 같다.
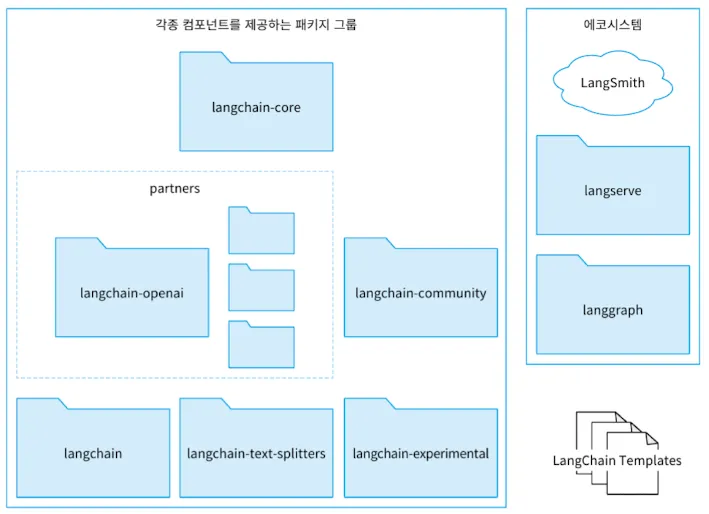
- 각 패키지는 다음과 같은 역할을 담당한다.
- langchain-core: LangChain 기반이 되는 추상화와 LangChain Expression Language(LCEL)를 제공한다. 이를 통해 다양한 언어 모델과 벡터 DB를 통일된 인터페이스로 활용할 수 있다.
- partners, langchain-community
- langchain-core가 제공하는 추상 기본 클래스에 대한 구현이 포함된다.
- 다양한 언어 모델과 오픈 소스에 대한 구현이다.
- partners 패키지로 독립되지 않은 것들은 langchain-community 패키지에 제공된다.
- langchain-core가 제공하는 추상 기본 클래스에 대한 구현이 포함된다.
- langchain, langchain-text-splitters, langchain-experimental
- langchain: 특정 유스케이스에 특화된 기능을 제공한다.
- langchain-text-splitters: 텍스트를 ‘청크’라는 단위로 분할하는 기능
- langchain-experimental: 연구, 실험 목적의 코드나 알려진 취약점(CVE)를 포함하는 코드
1. LangChain 초기 설정
- LangChain을 사용할 때는 필요한 최소 패키지만 설치해 사용하면 된다.
- LangChain에서 OpenAI의 Chat Completions를 사요한다면 langchain-core, langchain-openai만 설치하면 된다.
1
pip install langchain-core langchain-openai - LangSmith는 LangChain에서 공식적으로 제공하는 플랫폼이다. 디버깅, 테스트, 평가, 모니터링을 도와준다.
- LangSmith는 API 키를 발급 받고 다음과 같이 설정해주면 된다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
import os from dotenv import load_dotenv load_dotenv() os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true" os.environ["LANGCHAIN_ENDPOINT"] = "https://'api.smith.langchain.com" os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = os.getenv("SMITH_API_KEY") os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = "agent-book"
2. LangChain 주요 컴포넌트
- LangChain이 가진 컴포넌트는 다음과 같다.
- LLM/Chat model: 다양한 언어 모델과의 통합
- Prompt template: 프롬프트의 템플릿
- Example selector: Few-shot 프롬프팅의 예시를 동적으로 선택
- Output parser: 언어 모델의 출력을 지정한 형식으로 변환
- Chain: 각종 컴포넌트를 사용한 처리의 연쇄
- Document loader: 데이터 소스에서 문서를 읽어 들인다
- Document transformer: 문서에 어떤 변환을 가한다.
- Embedding model: 문서를 백터화한다
- Vector store: 벡터화한 문서의 저장소
- Retriever: 입력 텍스트와 관련된 문서를 검색
- Tool: Function calling 등에서 모델이 사용하는 함수를 추상화
- Toolkit: 함께 사용하는 것을 가정한 Tool의 컬렉션
- Chat history: 대화 이력의 저장소로서 각종 데이터베이스와 통합
2.1 LLM/Chat model
- 언어 모델을 공통된 인터페이스로 사용하는 방법을 제공한다.
2.1.1 LLM
- 하나의 텍스트 입력에 대해 하나의 텍스트 출력을 반환하는 컴포넌트다.
- 채팅이 아닌 언어 모델을 다룬다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
from langchain_openai import OpenAI
model = OpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
api_key=OPEN_API_KEY, # 환경변수
)
output = model.invoke("hi")
print(output)
2.1.2 Chat model
- 채팅 형식의 대화를 입력받아 응답하는 형식의 언어 모델을 다루기 위한 컴포넌트이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage, SystemMessage
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
model = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
api_key=OPEN_API_KEY
)
messages = [
SystemMessage("You are a helpful assistant."), # "role": "system"에 대응
HumanMessage("Hi, I'm Steven."), # "role": "user" 에 대응
AIMessage(content="Hello, Steven. What can I do for you?"), # "role": "assistant"에 대응
HumanMessage(content="What is my name?")
]
response = model.invoke(messages)
print(response)
2.1.3 스트리밍
- UX목적으로 스트리밍 응답을 얻고자 할 때 다음과 같이 할 수 있다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
model = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
api_key=OPEN_API_KEY
)
messages = [
SystemMessage("You are a helpful assistant."),
HumanMessage("Hi, I'm Steven."),
]
for chunk in model.stream(messages):
print(chunk.content, end="", flush=True)
2.1.4 LLM과 Chat model의 상속 관계
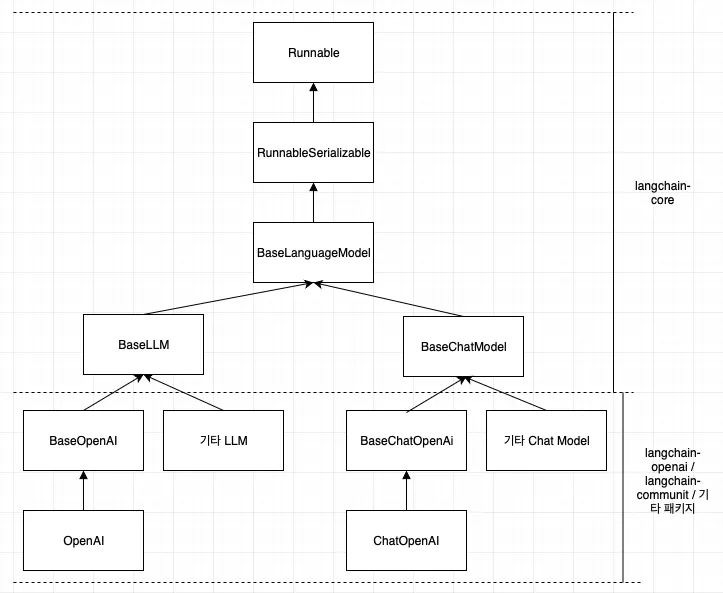
- LangChain은 위와 같은 관계를 가지기에 필요에 따라 langchain-openai 부분을 다른 패키지로 바꾸기 용이하다.
- 또 한, BaseLLM, BaseChatModel을 테스트를 위한 Fake 객체로 사용할 수도 있다.
2.2 PromptTemplate
- 프롬프트 처리를 추상화한 컴포넌트이다.
2.2.1 PromptTemplate
- 프롬프트를 템플릿화할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("""
Tell me the recipe for this dish. Name of the dish: {dish}
""")
prompt_value = prompt.invoke({
"dish": "pizza"
})
# output: Tell me the recipe for this dish. Name of the dish: pizza
print(prompt_value.text)
2.2.2 ChatPromptTemplate
- 채팅 형식 모델에 사용하는 템프릿이다. SystemMessage, HumanMessage, AIMessage를 각각 템플릿화해서 ChatPromptTemplate이라는 클래스로 함께 다룰 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Tell me the recipe for the dish user entered"),
("human", "{dish}"),
])
prompt_value = prompt.invoke({
"dish": "pizza"
})
# output: messages=[SystemMessage(content='Tell me the recipe for the dish user entered', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}), HumanMessage(content='pizza', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={})]
print(prompt_value)
2.2.3 MessagPlaceholder
- 채팅 이력 처럼 여러 메시지가 들어가는 placeholder를 두고 싶을 때 사용한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful assistant."),
MessagesPlaceholder("chat_history", optional=True),
("human", "{input}"),
])
prompt_value = prompt.invoke({
"chat_history": [
HumanMessage(content="Hello, I'm Steven."),
AIMessage(content="Hello Steven. What can I do for you?"),
],
"input": "What is my name?",
})
# output: messages=[SystemMessage(content='You are a helpful assistant.', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}), HumanMessage(content="Hello, I'm Steven.", additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}), AIMessage(content='Hello Steven. What can I do for you?', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}), HumanMessage(content='What is my name?', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={})]
print(prompt_value)
2.3 Output parser
- LLM 출력을 프로그램에서 파싱해 사용하고 싶을 때 사용된다.
- 응답을 Python 객체로 변환하거나 Json 등 포맷으로 출력을 지정할 수 있다.
2.3.1 PydanticOutputParser를 사용한 Python 객체 변환
- 출력을 python 객체로 변환할 때 사용한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Recipe(BaseModel):
ingredients: list[str] = Field(description="Ingredients of the dish")
steps: list[str] = Field(description="Steps to make the dish")
output_parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Recipe)
# Recipe 클래스에 대응하는 출력 형식을 지정하는 문자열에 대한 출력 형식 설명문
format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
print(format_instructions)
# 출력 설명문:
'''
The output should be formatted as a JSON instance that conforms to the JSON schema below.
As an example, for the schema {"properties": {"foo": {"title": "Foo", "description": "a list of strings", "type": "array", "items": {"type": "string"}}}, "required": ["foo"]}
the object {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]} is a well-formatted instance of the schema. The object {"properties": {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]}} is not well-formatted.
Here is the output schema:
{“properties”: {“ingredients”: {“description”: “Ingredients of the dish”, “items”: {“type”: “string”}, “title”: “Ingredients”, “type”: “array”}, “steps”: {“description”: “Steps to make the dish”, “items”: {“type”: “string”}, “title”: “Steps”, “type”: “array”}}, “required”: [“ingredients”, “steps”]}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
'''
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
(
"system",
"Please think of the recipe for the dish you entered.\n\n"
"{format_instructions}",
),
("human", "{dish}"),
])
# 출력을 지정하는 설명문을 프롬프트에 추가
prompt_with_format_instructions = prompt.partial(
format_instructions = format_instructions
)
prompt_value = prompt_with_format_instructions.invoke({"dish": "pizza"})
print("=== role: system ===")
print(prompt_value.messages[0].content)
print("=== role: user ===")
print(prompt_value.messages[1].content)
# 출력:
'''
=== role: system ===
Please think of the recipe for the dish you entered.
The output should be formatted as a JSON instance that conforms to the JSON schema below.
As an example, for the schema {"properties": {"foo": {"title": "Foo", "description": "a list of strings", "type": "array", "items": {"type": "string"}}}, "required": ["foo"]}
the object {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]} is a well-formatted instance of the schema. The object {"properties": {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]}} is not well-formatted.
Here is the output schema:
{“properties”: {“ingredients”: {“description”: “Ingredients of the dish”, “items”: {“type”: “string”}, “title”: “Ingredients”, “type”: “array”}, “steps”: {“description”: “Steps to make the dish”, “items”: {“type”: “string”}, “title”: “Steps”, “type”: “array”}}, “required”: [“ingredients”, “steps”]}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
=== role: user ===
pizza
'''
model = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
api_key=OPEN_API_KEY
)
ai_message = model.invoke(prompt_value)
# 출력을 Pandaic 모델 인스턴스로 변환
recipe = output_parser.invoke(ai_message)
print(type(recipe))
print(recipe)
# 출력:
'''
<class '__main__.Recipe'>
ingredients=['2 cups all-purpose flour', '1 packet (2 1/4 teaspoons) active dry yeast', '1 teaspoon sugar', '1 teaspoon salt', '3/4 cup warm water', '1 tablespoon olive oil', '1 cup pizza sauce', '2 cups shredded mozzarella cheese', 'Toppings of your choice (pepperoni, bell peppers, onions, mushrooms, etc.)']
steps=['In a bowl, combine warm water, sugar, and yeast. Let it sit for about 5 minutes until frothy.', 'In a large mixing bowl, combine flour and salt. Make a well in the center and add the yeast mixture and olive oil.', 'Mix until a dough forms, then knead on a floured surface for about 5-7 minutes until smooth.', 'Place the dough in a greased bowl, cover with a cloth, and let it rise in a warm place for about 1 hour or until doubled in size.', 'Preheat the oven to 475°F (245°C).', 'Roll out the dough on a floured surface to your desired thickness and shape.', 'Transfer the rolled dough to a pizza stone or baking sheet.', 'Spread pizza sauce evenly over the dough, leaving a small border for the crust.', 'Sprinkle shredded mozzarella cheese over the sauce, then add your desired toppings.', 'Bake in the preheated oven for 12-15 minutes or until the crust is golden and the cheese is bubbly.', 'Remove from the oven, let it cool for a few minutes, slice, and serve.']
'''
- 다만 LLM이 불완전한 JSON을 반환하면 오류가 발생할 수 있다. 때문에 with_strucuted_output을 사용하는 것이 더 좋다.
2.3.2 with_structed_output
- with_structed_output은 답변을 지정한 형식으로 강제할 수 있다. 때문에 출력 형식 프롬프트에만 의존하는 PydanticOutputParser 보다 정확도가 높다.
- 다만, with_structed_output을 지원하지 않는 chat model도 존재해 사용 전에 확인이 필요하다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class Recipe(BaseModel):
ingredients: list[str] = Field(description="Ingredients of the dish")
steps: list[str] = Field(description="Steps to make the dish")
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
(
"system",
"Please think of the recipe for the dish you entered.\n\n"
),
("human", "{dish}"),
])
model = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
api_key=OPEN_API_KEY
)
chain = prompt | model.with_structured_output(Recipe)
recipe = chain.invoke({"dish": "pizza"})
print(type(recipe))
print(recipe)
# 출력:
'''
<class '__main__.Recipe'>
ingredients=['2 1/4 cups all-purpose flour', '1 packet (2 1/4 tsp) active dry yeast', '1 tsp sugar', '1 tsp salt', '3/4 cup warm water (110°F)', '1 tbsp olive oil', '1 cup pizza sauce', '2 cups shredded mozzarella cheese', 'Toppings of choice (pepperoni, bell peppers, onions, mushrooms, etc.)'] steps=['In a small bowl, combine warm water, sugar, and yeast. Let it sit for about 5-10 minutes until frothy.', 'In a large mixing bowl, combine flour and salt. Make a well in the center and add the yeast mixture and olive oil.', 'Mix until a dough forms, then knead on a floured surface for about 5-7 minutes until smooth and elastic.', 'Place the dough in a greased bowl, cover with a damp cloth, and let it rise in a warm place for about 1 hour or until doubled in size.', 'Preheat your oven to 475°F (245°C).', 'Once the dough has risen, punch it down and roll it out on a floured surface to your desired thickness.', 'Transfer the rolled-out dough to a pizza stone or baking sheet.', 'Spread pizza sauce evenly over the dough, leaving a small border around the edges.', 'Sprinkle shredded mozzarella cheese over the sauce, then add your desired toppings.', 'Bake in the preheated oven for 12-15 minutes or until the crust is golden and the cheese is bubbly.', 'Remove from the oven, let it cool for a few minutes, slice, and serve.']
'''
2.4 Chain - LangChain Expression Language (LCEL) 개요
- LLM 애플리케이션은 다양한 이유로 단일 출력에서 그치지 않고, 연쇄 처리를 해야하는 경우가 있다.
- ex)
- LLM 출력을 얻은 뒤 해당 내용이 서비스 정책에 위반되지 않는지 확인
- LLM 출력 결과를 바탕으로 SQL을 실행한다
- ex)
- 이런 연쇄 처리를 LangChain에서 구현할 수 있게 한것이 LCEL이다.
-
LCEL은 프롬프트나 LLM을 ‘ ’를 이용해 연결해 Chain을 구현한다.
2.4.1 prompt와 model 연결
- 가장 단순한 예로 prompt와 이를 실행할 model을 연결할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "Please think of the recipe for the dish you entered.\n"),
("human", "{dish}")
])
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0, api_key=OPEN_API_KEY)
# model로 prompt 실행 후 결과를 StrOutputParser로 파싱
chain = prompt | model | StrOutputParser()
# invoke 반환은 AIMessage 객체이지만
# Chain에서 StrOutputParser를 사용해 AIMessage를 문자열로 변환
output = chain.invoke({"dish", "pizza"})
print(output)
- 다음과 같이 PydanticOutputParser를 이용해서 출력을 객체로 바꿀 수도 있다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
class Recipe(BaseModel):
ingredients: list[str] = Field(description="Ingredients of the dish")
steps: list[str] = Field(description="Steps to make the dish")
output_parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Recipe)
# Recipe 클래스에 대응하는 출력 형식을 지정하는 문자열에 대한 출력 형식 설명문
format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
print(format_instructions)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
(
"system",
"Please think of the recipe for the dish you entered.\n\n"
"{format_instructions}",
),
("human", "{dish}"),
])
prompt_with_format_instructions = prompt.partial(
format_instructions = format_instructions
)
model = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
api_key=OPEN_API_KEY
).bind(
response_format = {"type": "json_object"}
)
chain = prompt_with_format_instructions | model | output_parser
recipe = chain.invoke({"dish": "pizza"})
print(type(recipe))
print(recipe)
3. LangChain의 RAG 관련 컴포넌트
- LLM은 특정 시점 이후의 지식을 알지 못한다. 여기에 더해 새로운 정보나 비공개 정보를 포함한 답변을 원할 때 프롬프트에 문맥(context)을 추가하는 방법을 고려할 수 있다.
- 하지만 LLM은 토큰 수 최댓값 제한이 있기 때문에 모든 데이터를 context에 넣을 수 없다.
- 입력에 기반해 문서를 검색하고, 검색 결과를 context에 포함해 답변하는 기법을 RAG(Retrieval-Argumented Generation)이라 한다.
- RAG는 다음과 같이 벡터 DB에 문서를 저장해두고, 입력과 가까운 문서를 문맥에 포함시키는 형태를 가진다.
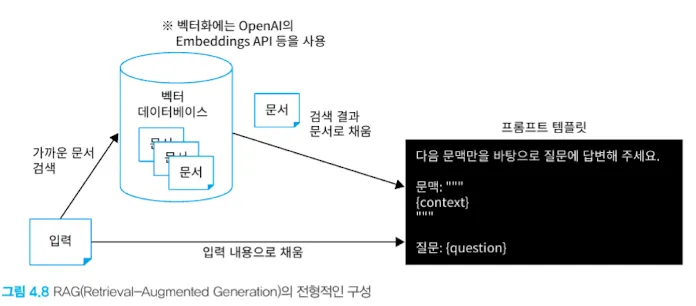
3.1 LangChain의 RAG 관련 컴포넌트 개요
- LangChain에서 제공하는 RAG관련 주요 컴포넌트는 다음과 같다
- Document loader: 데이터 소스에서 문서를 읽어 들인다
- Document transformer: 문서에 어떤 변환을 가한다
- Embedding model: 문서를 벡터화한다
- Vector store: 벡터화한 문서의 저장소
- Retriever: 입력 텍스트와 관련 있는 문서를 검색한다
- 위 컴포넌트들은 소스 데이터 저장과 검색에 다음과 같이 사용된다.
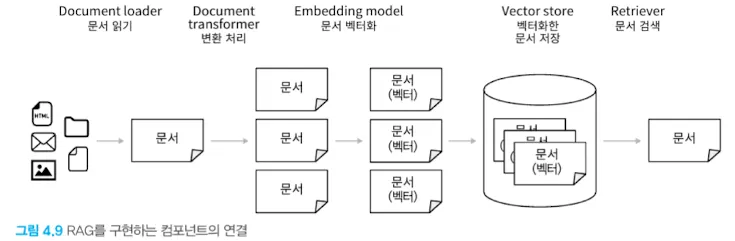
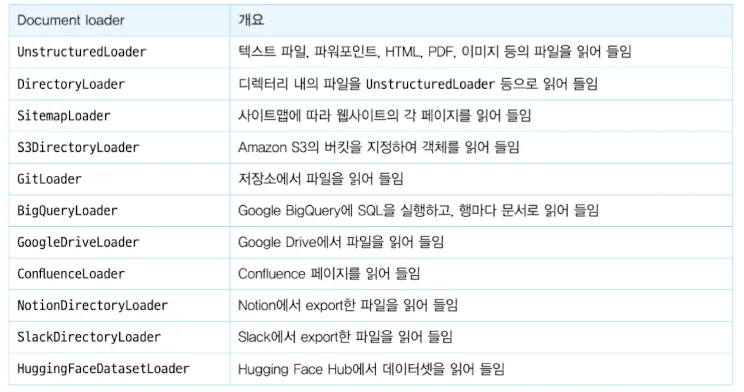
3.1.1 Document loader
- 데이터 읽기에 사용된다. 읽어들인 데이터를 문서라고 한다.
- 모든 Document loader는 BaseLoader의 구현체이다
- 현재 lang chain이 지원하는 document loader 항목은 링크에서 확인할 수 있다.
- 이 중 주요 로더는 다음과 같다
 ```python
```python
pip install langchain-community GitPython
from langchain_community.document_loaders import GitLoader
- 이 중 주요 로더는 다음과 같다
def file_filter(file_path: str) -> bool: return file_path.endswith(“.md”)
loader = GitLoader( clone_url=”https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain”, repo_path=”./langchain”, branch=”master”, file_filter=file_filter, )
raw_docs = loader.load() print(len(raw_docs))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
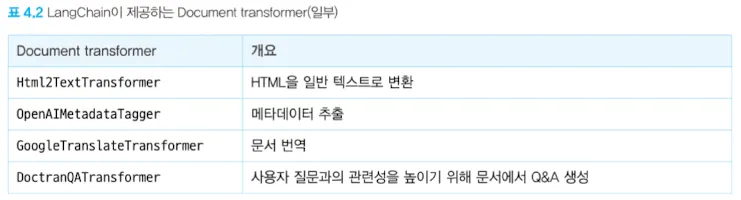
### 3.1.2 Document transformer
- Document loader로 읽어들인 문서에 변환을 가하는 역할을 한다.
- langchain-text-splitters 패키지를 설치해서 문서를 청크화할 수 있다. 이를 통해 입력 토큰 수를 줄이거나 보다 정확한 답변을 얻을 수 있다.
- 다양한 splitter: https://docs.langchain.com/oss/python/integrations/splitters
```python
from langchain_text_splitters import CharacterTextSplitter
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000,
chunk_overlap=0
)
docs = text_splitter.split_documents(raw_docs)
print(len(docs))
3.1.3 Embedding model
- 문서를 벡터화한다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
# OpenAI Embeddings API를 사용해서 text-embedding-3-small 이라는 모델로 벡터화한다.
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(
model="text-embedding-3-small",
api_key=OPEN_API_KEY,
)
query = "Is there any document loader for reading data from AWS s3?"
# 벡터화 시도, 실제 문서 벡터화 처리는 Vector store 클래스에서 데이터 저장 시 자동 실행된다.
vector = embeddings.embed_query(query)
print(len(vector))
print(vector)
3.1.4 Vector store
- 문서를 벡터화하여 저장한다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# Chroma 라는 로컬에서 사용 가능한 vector store 사용
# 이 외에도 Faiss, Elasticsearch, Redis 등을 vector store로 사용할 수 있다.
from langchain_chroma import Chroma
# 청크로 분할한 문서와 embedding model을 기반으로 Vector store 초기화
db = Chroma.from_documents(docs, embeddings)
# vector store의 인스턴스 생성
retriever = db.as_retriever()
query = "Is there any document loader for reading data from AWS s3?"
context_docs = retriever.invoke(query) # 쿼리와 가까운 문서 검색
print(f"len = {len(context_docs)}")
first_doc = context_docs[0]
print(f"metadata = {first_doc.metadata}")
print(first_doc.page_content)
3.2 LCEL을 사용한 RAG Chain 구현
- LCEL을 사용해서 문서 검색 결과를 PromptTemplate에 문맥으로 포함해 LLM에게 질문하고 답변을 받을 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template('''\
다음 문맥만을 바탕으로 질문에 답변해 주세요.
문맥: """
{context}
"""
질문: """
{question}
"""
''')
model = ChatOpenAI(
model_name="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
api_key=OPEN_API_KEY,
)
chain = (
# 입력이 retriever에 전달되면서 prompt에도 전달된다.
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| model
| StrOutputParser()
)
output = chain.invoke(query)
print(output)